The history of astrology can be traced to the ancient Babylonians. They were the first to relate myths to the constellations and define the signs of the zodiac. The Egyptians and then the Greeks refined this system. Astrology has also been a part of other ancient cultures. The name astrology “asteri” means star in Greek. In different parts of the world, the knowledge of astronomy and astrology have grown together.
Mesopotamian And Babylonian Astrology
Babylonian astrology dates back to the 2nd century. The people of Mesopotamia recognised five stars as well as the Sun and the Moon. They practised a form of prediction called the Enuma Anu Enlil. The earlier forms of astrology were largely omen based. The minutes and seconds by which we measure the zodiac originated from the Babylonian number system. It was the ancient Babylonians who divided the heavens into the twelve signs or constellations. The Greeks were the ones who later named these twelve divisions as the zodiac. The Babylonians used astrology for generalised predictions for the entire nation which is what we now refer to as mundane astrology.
Greek Astrology
The Greeks added much to the fields of astronomy and astrology. Astrology still benefits from the links to Greek gods. It is believed that when Alexander the Great’s conquests spread to Asia the Greeks were exposed to the knowledge of astrology that was present in the areas that they conquered such as Babylon, Syria and Persia. They changed the script of astrology to Greek.
Hipparchus, a Greek astronomer invented trigonometry and the precession of the equinoxes. The Greek mathematician, astronomer and astrologer Ptolemy wrote the Tetrabiblios. He defined the planets, houses, signs and aspects in detail as well as their function. His definitions are still relevant to the modern practice of Western astrology. Ptolemy also explained the system by which the zodiac related to and aligned with the solstices and equinoxes. He also explained how and why planets appeared to slow, speed and retrograde from the perspective of the earth.
The Roman Empire
The Romans did not add any innovations to the practice of astrology. But, their records and documentation of the same have survived better. We have the Astronomica which is a poem by Marcus Manilius that covers many aspects of astrology. The poem on astrology by Dorotheus of Sidon describes the concept of Triplicities.
Egyptian Astrology
Hellenistic Egypt saw great developments in astrology. We see that there are depictions of the twelve signs of the Zodiac in ancient Egyptian bas reliefs. The Egyptians assigned importance to the heavenly bodies and their influence upon people. They used calendars that showed favourable and unfavourable days that resemble horoscopes. The pyramids were not only the resting places of the Pharaohs but also had astronomical significance. Their sloping corridors also functioned as sighting tubes for astronomical purposes.

Egyptian Constellations Bas Relief
Mayan Astronomy and Astrology
The ancient Mayans of Mexico also followed a system of astrology. The Caracol observatory has an ancient staircase that leads to windows. Each of these windows corresponds to the positions of the planets at various times of the year.

Arabian Astrology
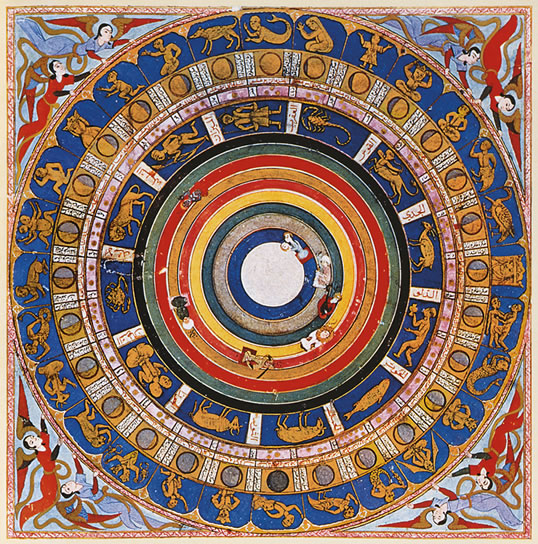
The Islamic world incorporated many of the Greek concepts of astrology into their practices. There was also a lot of sharing of knowledge between the Arabs and India. Between the 8th and 10th centuries, there was much study of these fields in Baghdad. Their scholars translated many works from Greek, Sanskrit and also Pahlavi to Arabic. They then refined all this knowledge particularly to suit the needs of their religion of Islam that specified that they would have to determine the time and direction of Mecca for prayer. So, they developed instruments and methods for calendars in response to this.

Indian Astrology
Jyotish or Indian astrology dates back to the Vedanga as a part of the Vedas to determine the time to conduct Vedic rituals. The Vedanga Jyotisha tracks the Sun and the Moon. The oldest surviving works on Indian astrology are the Brihat Samhita that dates to the early AD centuries. The classical period of Indian astrology is from the 5th century AD. Aryabhatta and Varahamihira wrote their classics on astrology in this time.

China
Chinese astronomy and calendars developed and grew in importance in the Han Dynasty of 2nd century BC to 2nd Century AD. The Chinese system of astrology is also closely linked with their system of philosophy. The 60-year cycle that combines the twelve animal signs of the zodiac with the five elements has been documented since Yin or Shing dynasty from 1766 BC to 1050 BC. Oracle bones that have the 60-year cycle and other details inscribed on them have also been found.